Return on assets (ROA) is an important valuation and growth metric for companies. If you want to understand a company's business, then determining the company's ROA is useful. Here, we cover the following topics to inform you about ROA and help you calculate it for any business:
- What is return on assets?
- Return on assets formula.
- Example of how to calculate return on assets.
- Frequently asked questions about return on assets.
- The significance of return on assets.

What is return on assets (ROA)?
Return on assets is a financial metric that tells you how much profit a company generates relative to the value of its assets. A company's assets encompass all of the resources that it owns or controls that produce business value.
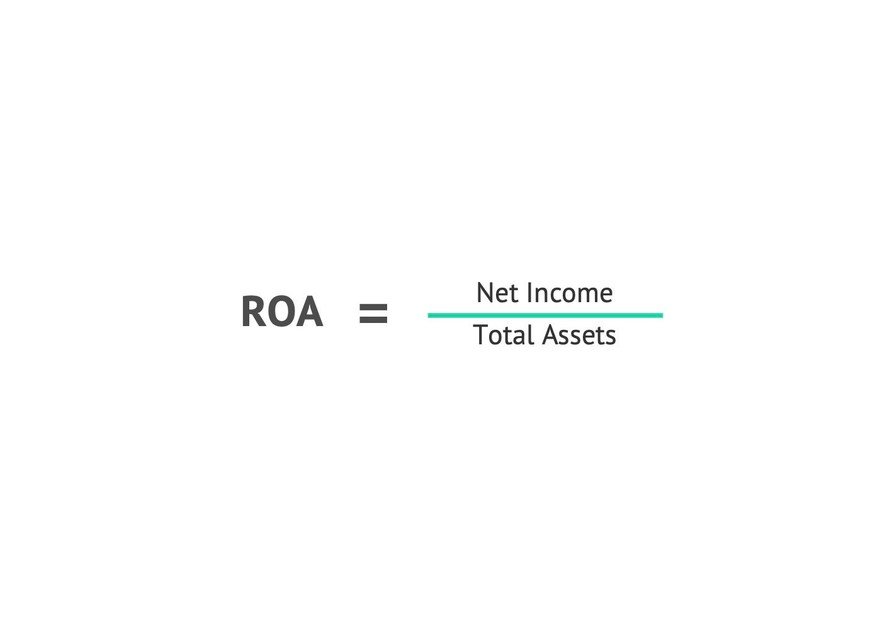
Return on assets formula
The formula for ROA, which is expressed as a percentage, is straightforward:
Example of how to calculate return on assets
There are two ways to calculate return on assets -- by using net income and total assets and by using net profit margin and asset turnover. All the numbers needed in these calculations can be obtained from a company's financial statements. We'll use 2020 results from healthcare giant Johnson & Johnson (NYSE:JNJ) as an example to illustrate both methods.
Calculating ROA using net income and total assets
- Find Johnson & Johnson's 2020 net income on its income statement. The income statement for 2020 is found in the company's latest 10-K (annual) report with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The Johnson & Johnson 10-K report for 2020 indicates that the company generated net income of $14.7 billion.
- Find the company's total assets on its balance sheet, which is also contained in the 10-K filing. J&J's total assets at the end of 2020 were valued at $174.9 billion.
- Divide Johnson & Johnson's net income by its total assets and then multiply that amount by 100. Net income of $14.7 billion divided by total assets of $174.9 billion gives a result of 0.084, which is multiplied by 100 to produce an ROA of 8.4% for the company in 2020.
Calculating ROA using net profit margin and asset turnover
- Find Johnson & Johnson's net income on its income statement. As noted in the example above, the company's net income in 2020 was $14.7 billion.
- Find the company's total revenue on its income statement. J&J's total revenue in 2020 was $82.6 billion.
- Calculate Johnson & Johnson's net profit margin by dividing its net income into its total revenue and multiplying that amount by 100. Divide the company's net income of $14.7 billion by its total revenue of $82.6 billion. Multiplying that amount by 100 yields a net profit margin for the company of 17.8%.
- Calculate the average value of the company's assets during the year. The 10-K report indicates that J&J's total assets were valued at $157.7 billion at the end of 2019. At the end of 2020, the company's total assets were worth $174.9 billion. The average of those two numbers -- $166.3 billion -- equals the company's average asset value during the period.
- Calculate asset turnover rate by dividing the company's total revenue into the average asset value and multiplying that amount by 100. Dividing the total revenue of $82.6 billion by the average asset value of $166.3 billion and converting that value into a percentage yields an asset turnover rate of 50%.
- Multiply Johnson & Johnson's net profit margin by its asset turnover rate to calculate its 2020 return on assets. The company's net profit margin of 17.8% times its asset turnover rate of 50% yields an ROA of 8.9%.
Return on assets vs. return on equity (ROE)
Return on assets is similar to another financial metric -- return on equity (ROE). Both ROA and ROE measure how well a business is performing. The key difference between the two is that ROE divides net income by shareholder's equity instead of by total assets as ROA does.
FAQ
Here are a couple of questions that frequently arise about return on assets:
Which ROA calculation method is better?
The ROA calculation method that uses only net income and total assets is simpler than the method that uses net profit margin and asset turnover. However, the latter method more accurately conveys a company's ROA throughout the reporting period, while the simpler method expresses a company's ROA only at the close of the period. And, using the more complex method enables you to learn more about the company by also determining its net profit margin and asset turnover rate.
What is considered a good ROA?
Generally speaking, ROA values of more than 5% are considered to be pretty good. An ROA of 20% or more is great. However, ROAs vary by industry, with some industries tending to have lower ROAs than others.
Related investing topics
The significance of return on assets
Return on assets is a useful metric because it provides insight on how effectively a company generates profits from its assets. Companies with high ROAs derive more profits from the same amount of assets than companies with low ROAs. The stocks of companies with high ROAs are more likely to perform well over the long term.