To find the right health coverage, you need to weigh the pros and cons of an HDHP vs. a PPO. The best choice for you depends on several factors, including your health, lifestyle, number of dependents, and financial situation.
Below, we'll look at all these factors to help you determine which type of insurance plan suits you.
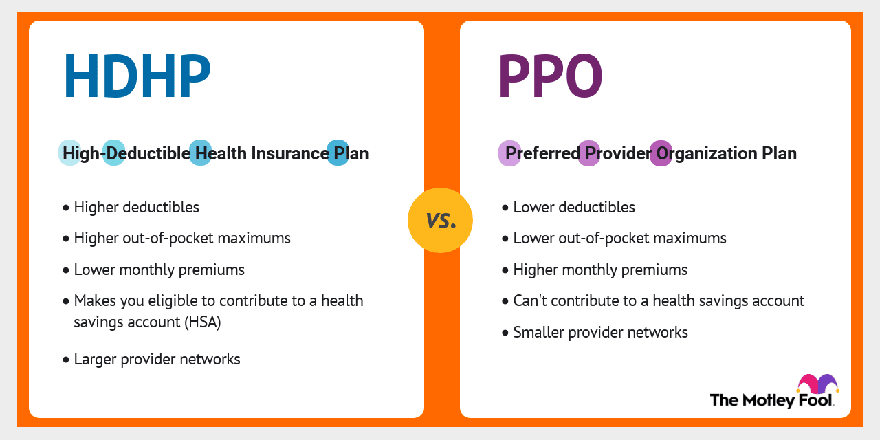
What is an HDHP?
HDHP stands for high-deductible health insurance plan. These are plans that have a deductible of $1,400 or more for individuals or $2,800 or more for families in 2021. As the name implies, these plans carry higher deductibles — the out-of-pocket costs you must meet before your insurance will pay the rest of your bill — than PPOs, which we'll discuss below. But they make up for this with lower monthly premiums, which is the monthly cost you pay for your insurance coverage.
These plans also tend to have higher out-of-pocket maximums than PPOs. Individual plans can carry out-of-pocket maximums of up to $7,000, while, if you're on a family plan, you could pay up to $14,000 in 2021 before your insurance coverage begins paying for 100% of your outstanding bills.
Because of these high deductibles, HDHPs typically aren't a great choice if you visit the doctor frequently. But they're great if you rarely need medical care and want to reduce your monthly payments.
Pros
- Lower monthly premiums.
- Makes you eligible to contribute to a health savings account (HSA).
- Larger provider networks.
Cons
- Higher deductibles — often thousands of dollars.
- Higher out-of-pocket maximums.
What is a PPO?
PPO stands for preferred provider organization plan. This type of health insurance plan offers lower deductibles than HDHPs. That makes them a good fit if you visit the doctor frequently and don't want to pay thousands of dollars out of pocket before your insurer will pay for care.
The downsides to these plans include higher premiums and smaller provider networks. The latter issue could pose a challenge if you travel often. If you become ill or injured and can't find an in-network provider near you, you could pay a lot more to see an out-of-network doctor.
Pros
- Lower deductibles.
- Lower out-of-pocket maximums.
Cons
- Higher premiums.
- Can't contribute to a health savings account.
- Smaller provider networks.
Comparing costs between HDHPs and PPOs
Ultimately, the type of health insurance plan that's cheapest for you will depend on how often you or your family members visit the doctor.
Consider the following example plans:
| HDHP | PPO | |
|---|---|---|
| Annual premiums | $4,800 | $6,000 |
| Deductible | $3,000 | $1,500 |
Chart by author.
No matter which type of plan you go with, you're going to have to pay your premiums if you want to keep your coverage. But you may not always have to pay your deductible.
If you don't go to the doctor at all, the HDHP is the clear winner. You'd save about $1,200 in premiums compared to going with the PPO plan. But if you had a $5,000 medical bill, you'd fare better with the PPO plan. You'd pay about $7,500 for your premiums and deductible compared to the $7,800 you'd pay for your premiums and deductible with the HDHP.
Of course, you can't always predict when you'll need medical care, so you should base your decision on your overall health. If you know you go to the doctor often, a PPO might make more sense. If you only see a doctor for emergencies, an HDHP might be cheaper.
It's worth noting that both HDHPs and PPOs also have copays, or coinsurance, in addition to premiums and deductibles. These aren't included in the example above. Coinsurance is a percentage of your hospital bill that you're responsible for even after meeting your deductible. This percentage can vary depending on the type of service required.
You continue to pay coinsurance until you reach your out-of-pocket maximum for the year, at which point your health insurance takes over for all covered costs going forward. It's important to keep this in mind when considering which health insurance plan is the right fit for you.
HDHPs and HSAs
Those with HDHPs can contribute to an HSA — a benefit denied to PPO policyholders. An HSA is a special type of savings account designed to house funds earmarked for medical expenses. They have several financial benefits, including:
- Contributions to an HSA reduce your taxable income for the year just like contributions to most 401(k)s and traditional IRAs.
- Some HSAs allow you to invest your funds as you could with a retirement account.
- If you use the money for medical expenses at any age, your withdrawals are tax-free.
- You can make non-medical withdrawals once you're age 65 (if you're younger than 65, you'll face a 20% penalty), although you'll pay taxes on the withdrawals.
- Unlike contributions to flexible spending accounts (FSAs), HSA contributions carry over from year to year.
- Some employers that offer HSAs also offer an HSA match, which is similar to a 401(k) match.
You may notice some similarities between an HSA and a retirement account. Although the HSA wasn't designed for this, it actually makes a pretty good retirement plan. So, even if you don't need your HSA funds for medical bills, you can still use that money without penalty once you get older.
In 2021, those with individual HDHPs may contribute up to $3,600 to an HSA, while those with family plans may contribute up to $7,200. These limits can change from year to year. In 2022, they will rise to $3,650 and $7,300, respectively.
Other considerations
If you're still having trouble deciding between an HDHP or a PPO, ask yourself the following questions:
- How often do you go to the doctor?
- Do you have any chronic health conditions?
- Do you have any planned medical expenses coming up such as the birth of a child or surgery?
- Are you looking for a plan for yourself or for your entire family?
- Is it important to you to have a large provider network to choose from?
The right answer for you could change from one year to the next. When you're nearing the end of your policy term, go back through this list of questions to see if anything's changed. Consider switching the type of health insurance you choose if you believe it will be more affordable.
Don't just base your choice on costs. Look into what each policy covers and make sure medications or treatments you or your family members need are covered. Compare several policies side by side to figure out which offers you the greatest value — that is, the most coverage at the most reasonable price. It takes some time, but it's the best way to make sure you find the best coverage for you.

















