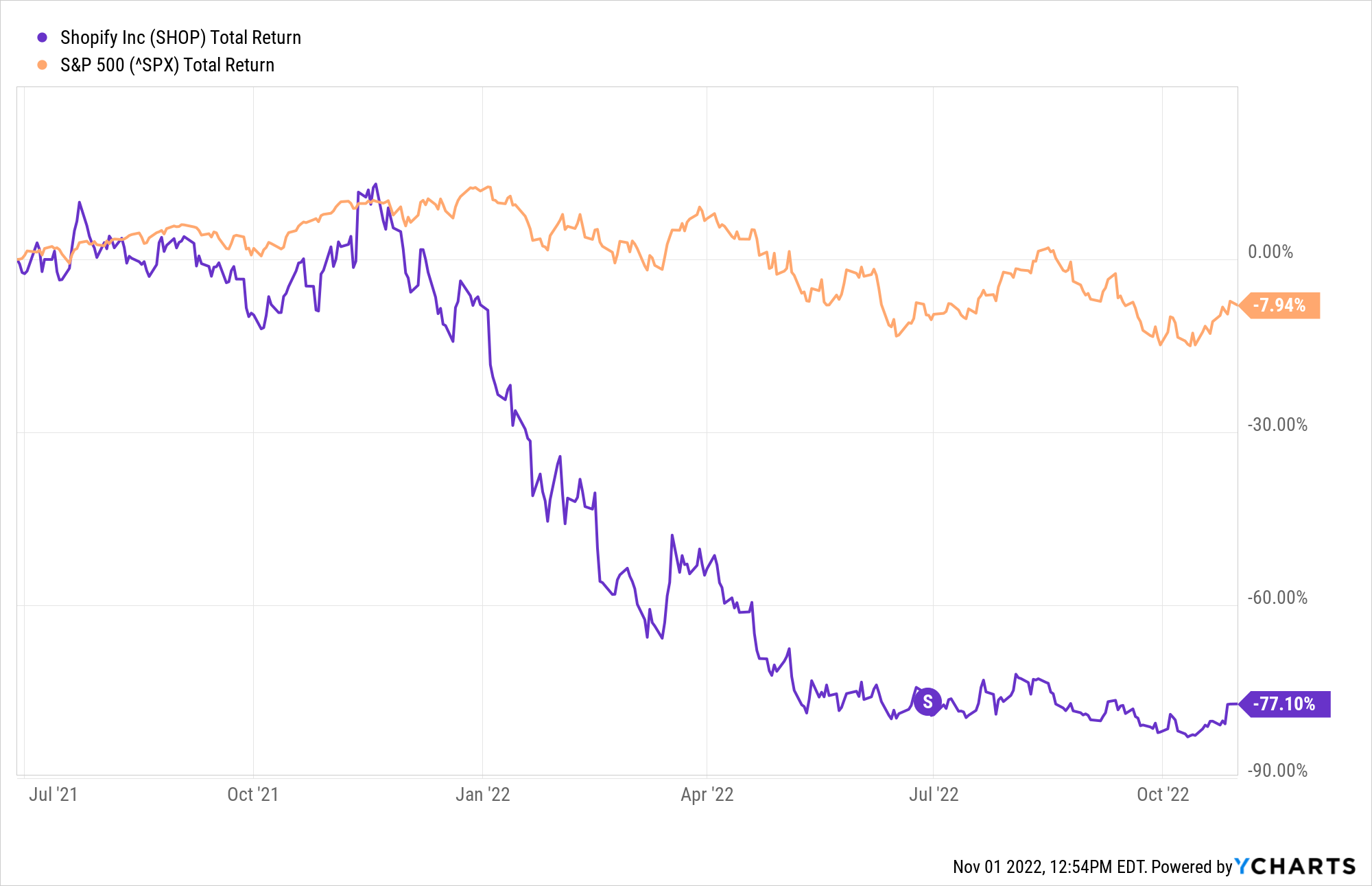
With a forward split -- the most common type of split -- the company increases the number of shares on the market. As a result, the share price decreases and potentially attracts more investors, increasing trading activity.
This seems positive, but does it actually affect the value of a stock? We've gone over the stock splits calendar, combed the data from five high-profile stock splits, and compared their performance to the S&P 500. Keep reading to see the results.
Key findings
- Stock splits don't affect the value of shares that you hold in a company.
- A stock split isn't a reliable indicator of whether a stock's value will increase or decrease.
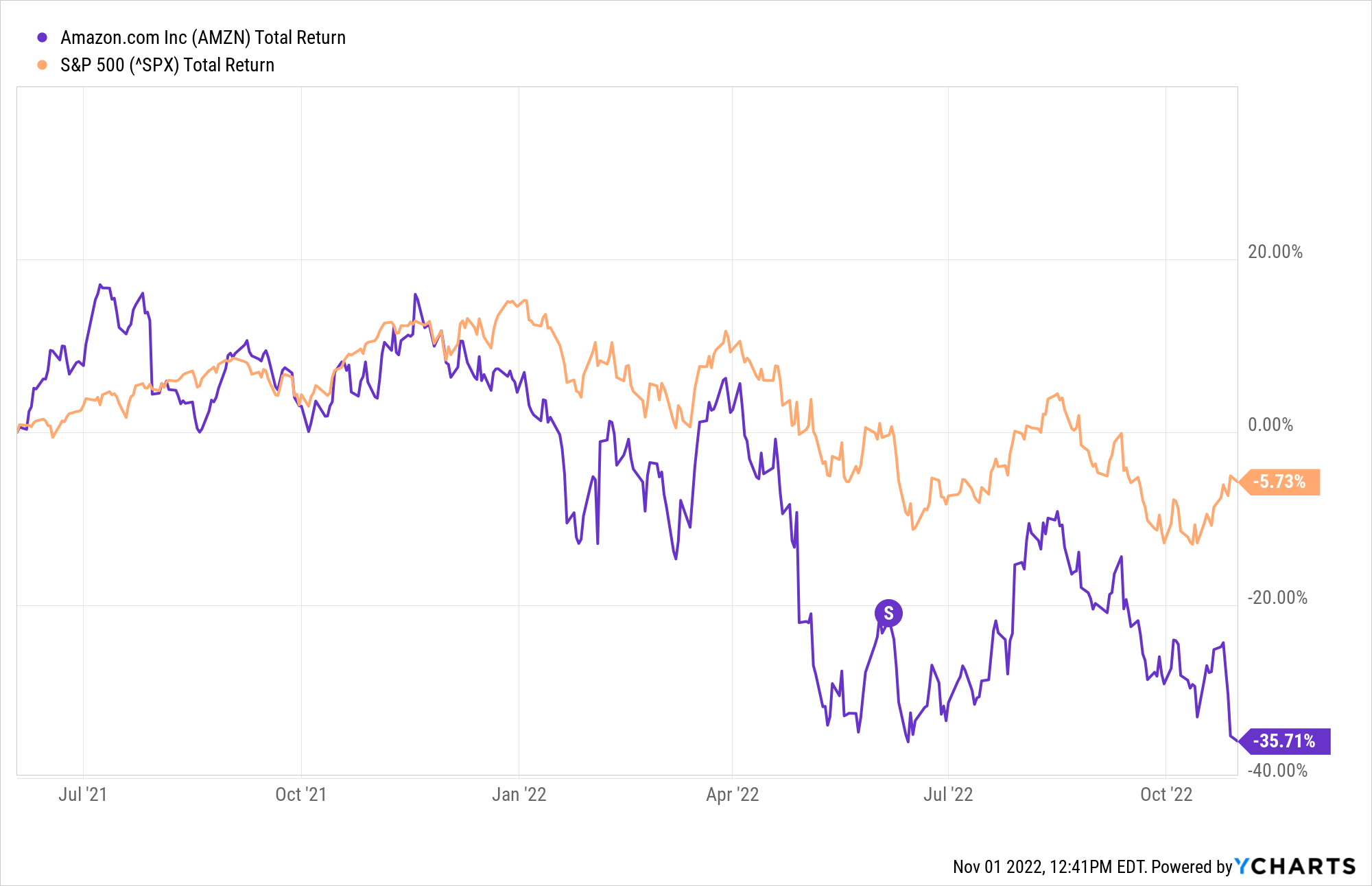
- Of the five stocks analyzed, only Amazon (AMZN +0.21%) outperformed the S&P 500 three months after its stock split, but it also fell behind over the long term.
- Shopify (NYSE:SHOP) had the worst results, with its share value dropping significantly (although this was a continuation of a longer trend).
- Changes in price that may look related to a stock split are often better attributed to longer-term or market trends.
What is a stock split?
A stock split is when a company multiplies or divides its share count. It doesn't change the company's market value or capitalization. If you own shares in the company, a stock split doesn't change the value of your holdings.
You can get many more details (including a video explanation) on What Are Stock Splits?
There are two types of stock splits:
- Forward stock split: A company increases its share count and issues new shares to existing investors. For example, in a 2-for-1 forward split, each investor's share count doubles and the share price is adjusted to half of its pre-split price.
- Reverse stock split: A company decreases its share count and replaces existing shares with a proportionally smaller number. For example, in a 1-for-2 reverse split, each investor's share count gets cut in half and the share price is adjusted to twice its pre-split price.
Forward stock splits are far more common, because they make it cheaper to buy shares in a company. Reverse stock splits don't happen nearly as much, and they're often due to a decline in the company's share price.
Do stock splits affect share value?
In a way, yes. The split does change the value of each share, but the number of shares held by any shareholder is also adjusted so that their total holdings have the exact same value as before the split.
But what about over the long term? Do stocks tend to go up or down before or after a split, and what does that mean for when you should buy? As you'll see in the following sections, any short-term changes around the time of a split are very minor compared to the long-term trends you should be watching as a Foolish investor.
Amazon's 2022 stock split
Tech giant Amazon announced a 20-for-1 stock split on March 9, 2022, at a time when its shares were trading for $2,785.58.
Amazon performed well initially after the announcement, with share prices rising 10.9% over the next month, compared to 4.9% for the S&P 500. However, prices fell from there.
Overall, from the March 9 announcement to the June 3 stock split, Amazon's share price decreased by 12.2%. The S&P 500 also decreased in value, but only by 4.0%. After the split, Amazon dipped and then recovered, as did the S&P, though the index didn't quite get back to positive.