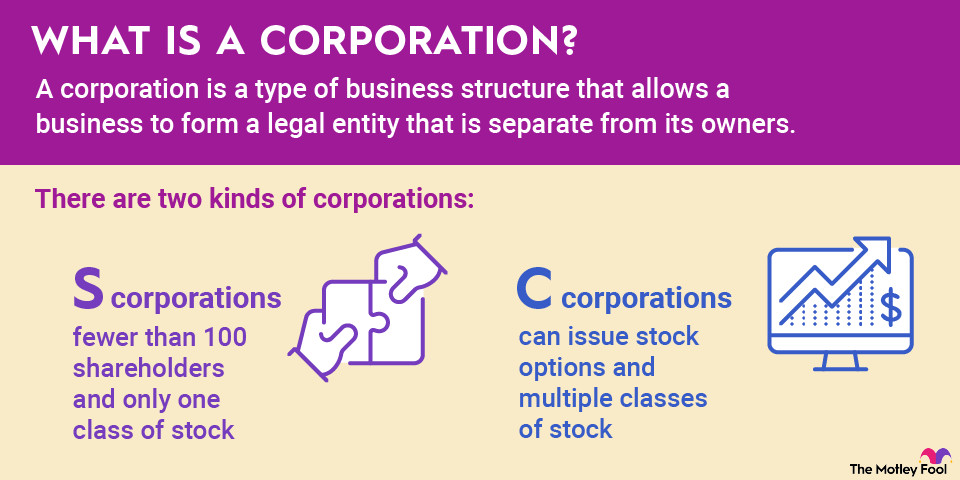
A collective bargaining agreement (CBA) is a contract between an employer and its employees that governs workplace terms, like wages, working hours, and hiring practices. The terms outlined in the CBA are agreed upon by both parties through negotiation, typically with a labor union representing the employees.

How CBAs are developed
CBAs result from a series of events. The exact steps can vary, but the common path includes:
- Conflict or expiration of prior agreement. A conflict between employers and employees regarding some aspect of working conditions can prompt employees to unionize and argue for change. If a CBA is already in place, its pending expiration would trigger a new round of employer-union negotiations. Note that an expired CBA remains in force until it is replaced with a new agreement.
- Preparation. Prior to negotiations, the employer and union will define their demands and choose someone to represent their side in the bargaining sessions.
- Negotiation. When a union is involved, the negotiation of labor terms is called collective bargaining. Federal law requires these negotiations to cover "mandatory subjects," or topics that directly affect wages, hours, and working conditions.
- Tentative agreement. Once negotiators reach an agreement, they document the terms in a draft CBA. Each side reviews the drafted terms and approves it or requests adjustments.
- Ratification. When all terms are settled, the union approves the CBA and submits it to union members for voting. If union members accept the terms, the CBA is finalized and executed. At that point, the agreement is legally binding.
CBA governance
Federal laws that govern the collective bargaining process include:
- National Labor Relations Act (NLRA). The NLRA covers private-sector workers outside the airline and railroad industries. The legislation was enacted in 1935 to protect workers' rights to join trade unions and bargain collectively. The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) oversees NLRA enforcement.
- Railway Labor Act (RLA). The RLA governs labor relations in the U.S. airline and railroad industries.
- Civil Service Reform Act of 1978. The Civil Service Reform Act established the Federal Labor Relations Authority (FLRA), which oversees collective bargaining and complaints of unfair labor practices for federal employees.
Additionally, states have statutes pertaining to CBAs and the collective bargaining process.
Disneyland Resort CBA
Even the happiest place on Earth has a contract in place to ensure acceptable working conditions. The latest agreement between Disneyland Resort and Workers United Local 50 is 92 pages long and covers 35 sections of terms. The document, effective from 2023 to 2028, amends and extends a CBA that was established between the resorts and the union in 1959.
Workers Union
The 2023 document mandates union membership as a condition of employment and outlines the employer's responsibility to withhold and remit union dues. In the employer's favor, the contract prohibits strikes or work stoppages.
Related investing topics
Other notable topics in the agreement include:
- Scheduling of work, including when employee work schedules are published, time off for each employee, and calculation of overtime pay
- The calculation and accrual of vacation time
- Paid holidays and eligibility for holiday pay
- Pension benefits, including the calculation of benefits and eligibility
- How seniority is defined and how it influences shift scheduling and other management decisions
- Drug and alcohol policy, including when employees can be tested for drug use
- Wage rates by job role
The contract is executed by the director of labor relations for Walt Disney Parks and Resorts and the president of Workers United Local 50.